
This operation works on the selected files only, so you need If you need to send someone else your project tree structure, butĬontaining only the files which have changed. You can export a change tree, which is useful

Where xxxxxxx is revision 1 short hash and yyyyyyy revision is 2 short hash. You can Revert selected files to version 1 or version 2.Ĭontext menu → Revert to revision xxxxxxx / Revert to revision yyyyyyy You to compare them individually using context menu. This dialog shows a list of all files which have changed and allows TortoiseGit context menu → Diff with previous version
Diffmerge ignore whitespace windows#
or in Windows Explorer, when you select no files or a folder In log dialog, when you select two commitsĬontext menu → Compare with previous version / Compare with working tree Naturally, any line with changed content is always included in Was none before, or removing a whitespace completely is still Includes all changes in indentation and inline whitespace asĮxcludes changes which are due solely to a change in theĪmount or type of whitespace, eg. Section 2.17.3, “Comparing Version”), as well as in the settings forĮxcludes changes which are due solely to difference in line-end style. You will see these settings in the Comparing Versionĭialog (cf. These changes when it comes to comparing and applying differences.
Unfortunately this will markĪ large number of lines as changed, even though there is no change Sometimes in the life of a project you might change the line endingsĬhange the indentation of a section. Read Section 2.36.4, “External Program Settings” toįind out about configuring other diff tools. If you have configured a third party diff tool, you can use Viewing differences between directory hierarchies. The built-in tools supplied with TortoiseGit do not support You can also select two branches and compare those using the context menu as described in Section 2.11, “Browse All Refs”. There you can click on one branch and select Compare to working tree to see all changes between that branch and your current state of the working tree. You can use the log dialog and select the two revisions as described above for "Difference between two previous revisions".Īn easier way is to open the reference browser (cf. (maybe the current one to another branch or two branches) If you want to see the changes of different branches Then from the explorer context menu select If you want to see the differences between two differentįiles, you can do that directly in explorer by selectingīoth files (using the usual Ctrl-modifier). From the Revision Logĭialog select the revision of interest, then select Is harder to read than a visual file compare, but will Only the differences with a few lines of context.
Diffmerge ignore whitespace Patch#
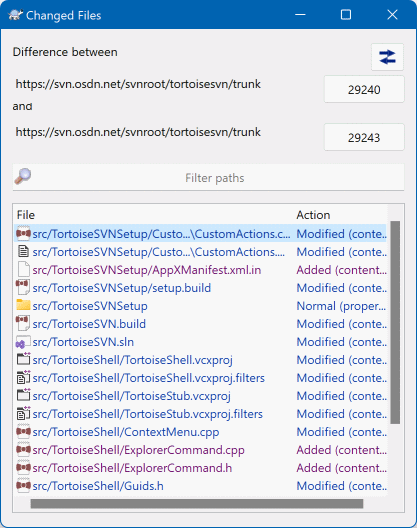
Use Unified-Diff output (GNU patch format). In a particular revision in one view, you can If you want to see the changes made to all files Of changed files (maybe with a folder filder pre-applied). Then the Compare Revisions dialog appears, showing a list If you want to see the difference between two revisionsĭialog and select the two revisions you want to compare It will not show changes newer than your working tree.ĭifference between two previous revisions To bring it to the state you now see in your working tree. This shows you the last change made to that file The last-commit-date (as recorded in your working tree) and the This will perform a diff between the revision before TortoiseGit → Diff with previous version. Hasn't been modified, just right click on the file. Revision and your working tree, assuming that the working tree

If you want to see the difference between the last committed Revision and your working tree, use the Logĭialog, select the revision of interest, then selectįrom the context menu (cf.

If you want to see the difference between a particular Have made in your working tree, just use the explorer If you want to see what (uncommitted) changes you


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
